Understanding the distinction between low voltage and line voltage is crucial for homeowners, businesses, and industry professionals when planning electrical installations and lighting solutions.
Lombardi Electric is the top destination for Alexandria commercial electrical services, Alexandria residential electrical services, and Alexandria industrial electrical services. We also offer lighting design and installation, as well as home automation services. Call 318-545-7575 to speak with one of our professional electricians today.
What is Low Voltage?

Low voltages refer to electricity that operates at significantly lower voltages than the standard household power, typically below 50 volts.
Benefits of Low Voltage Wiring
Low voltage wiring offers a range of advantages:
Operating at low voltages greatly reduces the risk of electrical shock. These are more energy-efficient than their high-voltage counterparts. It consumes less power, which not only contributes to energy savings.
Low-voltage wires are incredibly versatile and can be used in various settings. This wiring is suitable for precise applications where standard voltage might be excessive. Despite the initial investment in transformers and specialized equipment, the overall wiring and material costs for a low-voltage system are lower than standard voltage wiring. These wires are also generally easier and safer to install and modify.
Disadvantages of Low Voltage Wiring
There are certain drawbacks of using low voltage:
A low-voltage system is more susceptible to voltage drop, especially over long distances. It also has a limited power delivery, so it’s unable to support some electrical appliances and equipment.
Installing a low-voltage system often requires complex components, such as transformers and specific types of cabling. In some applications, there may be a more limited availability of components and fixtures than those for standard voltage. Although this can be more energy-efficient and cost-effective in the long run, the initial setup costs can be higher.
What is Line Voltage?
The term, line voltage, refers to the standard electrical voltage level supplied to residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Unlike a low-voltage system, this standard line voltage wiring does not require transformers to decrease voltage.
Benefits of Line Voltage Wiring
Line voltage wiring offers several distinct advantages:
Line voltage provides an immediate and direct connection to the power source. This ensures efficient and consistent power delivery. It is capable of high power capacity, making it ideal for commercial lighting and industrial equipment.
It can be used for various applications, from residential lighting to industrial tools.
Unlike low-voltage systems, it does not require transformers, making it easier to maintain and install. It can be more cost-effective upfront compared to low-voltage systems.
Disadvantages of Line Voltage Wiring
Despite its widespread use and advantages, line voltage wiring also has some drawbacks:
The primary concern is its increased risk of electrical shock and fire. Working with this wiring often requires professional expertise due to the complexities and dangers associated with high voltage.
This system type can be less energy-efficient than low-voltage alternatives.
Line voltage systems can be less flexible in terms of installation and layout. While the initial setup can be more straightforward and less expensive, it may incur higher long-term costs in certain scenarios.
Low Voltage vs. Line Voltage: What are the Main Differences?

Understanding the differences between low voltage and line voltage is crucial for making informed decisions.
Low voltage systems are known for their enhanced safety, energy efficiency, and suitability for specific applications, such as landscape applications and risk-averse situations. However, their limited power capacity and complex installation are notable drawbacks.
In contrast, line voltage is standard in most residential, commercial, and industrial settings. It is ideal for running household appliances and heavy machinery. These systems are simpler to install and maintain but have increased safety risks and may be less energy-efficient for low-power applications.
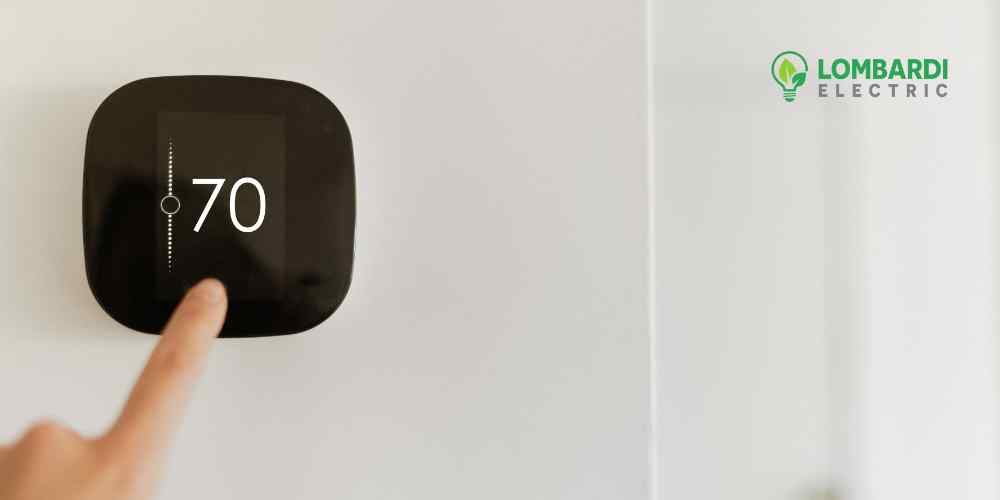
Low Voltage Thermostat and Line Voltage Thermostat
These thermostats are different temperature control devices suited for specific heating and air conditioning purposes. The choice between a low-voltage thermostat and a line-voltage thermostat depends on the specific requirements for thermostat regulation and energy efficiency in the given space.
What is a Low-Voltage Thermostat?
A low-voltage thermostat is used in central heating and cooling. Operating typically on 24 volts, low voltage thermostats are an integral part of HVAC systems.
Low-voltage thermostats are versatile, supporting various HVAC functions. The operation of the low-voltage thermostat makes it safer and more energy-efficient than its line-voltage thermostat counterpart.
Low-voltage thermostats come in various types, aligning with modern smart home technologies. So, a low-voltage thermostat is ideal for comprehensive climate control in a building, offering precise temperature regulation, energy savings, and enhanced user convenience.
What is a Line Voltage Thermostat?
A line voltage thermostat controls heating systems that operate directly on line voltage power. Line voltage thermostats are commonly used to control electric heaters, such as baseboard heaters, convectors, etc. There are two different types of line voltage thermostats: single-pole thermostat and double-pole thermostat.
- A Single Pole Thermostat has two wires and does not have an “off” setting; it only turns the heater down to a minimum temperature.
- A Double Pole Thermostat has four wires, offering high and low settings, including a true “off” position, allowing complete heater shutdown. This difference makes double-pole thermostats a safer and more versatile option.
Low Voltage and Line Voltage Outdoor Lighting
In terms of outdoor lighting, low voltage lighting systems and line voltage lighting systems have their distinct places and advantages.
Low-voltage lighting systems are particularly favored for landscape applications due to their safety and energy efficiency. Low-voltage lighting is ideal for creating ambient pathway lighting. Additionally, it’s preferred for outdoor lighting projects because it is easier to install and more energy efficient.
In contrast, line voltage lighting systems are better suited for larger, more open areas that require brighter, more intensive illumination. A line voltage system must be carefully installed.
The choice between a low voltage and line voltage outdoor lighting system ultimately hinges on the space’s specific needs.
Differences Between Low Voltage Lighting Systems and Line Voltage Lighting Systems

The difference between the line and low voltage lighting system includes:
Heading: Lifespan
The lifespan of low voltage lighting systems and line voltage lighting systems significantly differs, influencing their suitability for various applications:
Low voltage lighting offers a longer lifespan due to lower electrical stress, reducing bulb and fixture replacements, which is especially beneficial in display lighting applications. This is one of the many benefits of LED outdoor lighting.
In contrast, line voltage lighting has a shorter lifespan in high-intensity applications due to increased thermal stress.
Heading: Light Quality
The quality of light produced by line and low voltage lighting systems varies, impacting the ambiance and functionality of the lit space:
Low voltage lighting provides precise, crisp illumination with excellent color rendering, ideal for display lighting, whereas line voltage lighting delivers strong, bright light suitable for various applications.
Heading: Size and Style
The size and style of low voltage lighting fixtures and line voltage lighting fixtures differ, influencing their application and aesthetic integration in various settings:
Low-voltage light fixtures feature compact, sleek designs. In contrast, line voltage light figures tend to be larger due to higher power capacity.
Heading: Movability
Low-voltage fixtures are more movable and adaptable. Whereas line voltage lighting fixtures are less mobile due to larger size and higher requirements, often requiring professional assistance for reconfiguration.
Heading: Safety
The safety aspects of low voltage lighting systems and line voltage lighting systems are markedly different, influencing their suitability for various environments:
A low-voltage fixture will be safer since it operates at lower voltages, whereas line voltage fixtures are generally safe but pose higher risks.
Call Lombardi Electric Today
Whether you need advice on low-voltage or line-voltage systems for your home, business, or industrial setting, our team of experts is here to assist you. For Alexandria lighting design services that meet your unique needs, contact Lombardi Electric at 318-545-7575 today. Let us light up your world with expertise and care!